GoodWe Galaxy Series -- An Innovative Solution for Green Energy Transition in Cold Chain Vehicles
June 16, 2025
Why Do Cold Chain Vehicles Need PV Systems? Why Are Traditional Components Inadequate?
1.1 Energy Challenges in Cold Chain Vehicles
Cold chain transportation is critical for temperature-sensitive goods like food and pharmaceuticals, but traditional fuel-powered refrigeration systems face two major issues:
High Fuel Costs: Diesel generators consume 30-50 liters daily, accounting for over 30% of operational costs. Refrigeration increases engine load by 20%-30%, further raising fuel consumption. For example, data from Kühne+Nagel’s fleet shows refrigeration accounts for 40% of total fuel usage.
Carbon Emission Pressure: EU standards restrict cold chain vehicle emissions to 150g CO₂/km, which traditional systems struggle to meet. The EU-ETS II (effective 2025) will impose carbon quotas, potentially raising fuel costs by €0.3-0.5 per liter by 2027 as CO₂ prices exceed €100/ton.
1.2 Weakness of Traditional and Flexible PV Modules
Traditional Photovoltaic Modules
In the application scenario of vehicle - mounted photovoltaics, traditional photovoltaic modules have significant limitations due to their own characteristics. Their unit area weight is as high as 20 kg/㎡, and they rely on metal brackets for rigid installation. This installation method also significantly increases the wind resistance coefficient, which is 5%-8% higher than that of the original vehicle. This not only increases energy consumption but also has an adverse impact on the vehicle's cruising range and driving stability.
Flexible Thin-Film Modules
Flexible photovoltaic modules have poor impact resistance under complex road conditions and are easily damaged when encountering small stones or hail. Continuous vibration loads can cause periodic stress concentration inside them, leading to the expansion of micro - cracks. In a vibrating environment, the thermal stress of thin film solar cells can cause delamination at the interface between the electrode and the substrate, reducing photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Galaxy-Solution for cold chain vehicle
Galaxy Series Ultra-lightweight Solar Panel, with its unique technical characteristics, has become the exclusive preferred solution for cold chain scenario. The adaptability between its product technical characteristics and the scenario is specifically reflected in the following aspects:
Lightweight Design
The weight per unit area is only 5.6 kg/㎡, which is 72% lighter than traditional modules. This feature allows for direct installation on the vehicle roof without additional reinforcement, significantly reducing the modification cost and complexity. At the same time, with a thickness of only 5 mm, the module effectively reduces the wind resistance coefficient during vehicle driving, thereby reducing overall fuel consumption.
High Reliability Protection
The product surface is made of high-strength tempered glass, which has excellent load-bearing capacity. The maximum static load on both the front and back can reach 2400 Pa. It has passed strict hail-impact tests (hail with a diameter of 25 mm impacts at a speed of 23 m/s), and can effectively withstand the vibration and impact under complex road conditions as well as the influence of severe weather (such as hail and strong winds).
High Efficiency Power Generation Performance
Equipped with TOPCon battery technology, the Galaxy modules achieve high efficiency conversion of solar energy. They can convert light energy into electrical energy to the greatest extent within the limited vehicle roof space.
Convenient System
The installation solution using structural adhesive does not require punching through the top of the carriage, fundamentally avoiding the leakage risk that may be caused by traditional mechanical fixing methods. The installation process is efficient and fast. The installation time per square meter is only 3 minutes, significantly shortening the vehicle modification cycle.
Galaxy System Solution
Galaxy System Solution

Picture 1. Galaxy layout diagram on a certain truck
We designed this system based on the specific dimensions of the truck. This carriage is 13.75 meters long and 2.5 meters wide. Through our layout, 16 Galaxy products can be installed, with a power output of over 5.5KW.
In the plan, we use guide rails and EPDM rubber strips to raise the panels, ensuring the ventilation and heat dissipation capabilities of the panels. Meanwhile, the guide rails at the front and rear can also play a sealing role, preventing dust and other substances from entering the middle cavity. At the same time, we also use EPDM rubber strips for cable management to prevent the wires from coming into direct contact with the top of the carriage.
3.1 Time-saving solution
Installing a Galaxy PV system on the top of a cold-chain vehicle can significantly improve operational efficiency by reducing energy dependence. Traditional cold - chain transportation relies on diesel generators or on - board batteries for power supply, requiring frequent stops for charging or refueling. Especially during long - distance transportation, the average daily parking time for energy replenishment can reach 2 hours. The introduction of the photovoltaic system can recharge the on-board batteries in real-time and reduce dependence on diesel generators, thus reducing the parking time by 50% (for example, reducing the daily parking time by 1 hour as in the case). Calculated based on an average daily driving distance of 500 kilometers and a freight rate of 1 dollar per kilometer, an additional income of 50 dollars per hour can be generated (50 kilometers × 1 dollar). At the same time, the continuous power supply from the photovoltaic system extends the cruising range of the refrigeration system from 8 hours to 10 hours, expanding the single - trip transportation radius by 25%. This not only reduces the frequency of transshipment but also improves the coverage efficiency of the transportation network by extending the continuous operation time, achieving a double breakthrough in economy and operational flexibility.
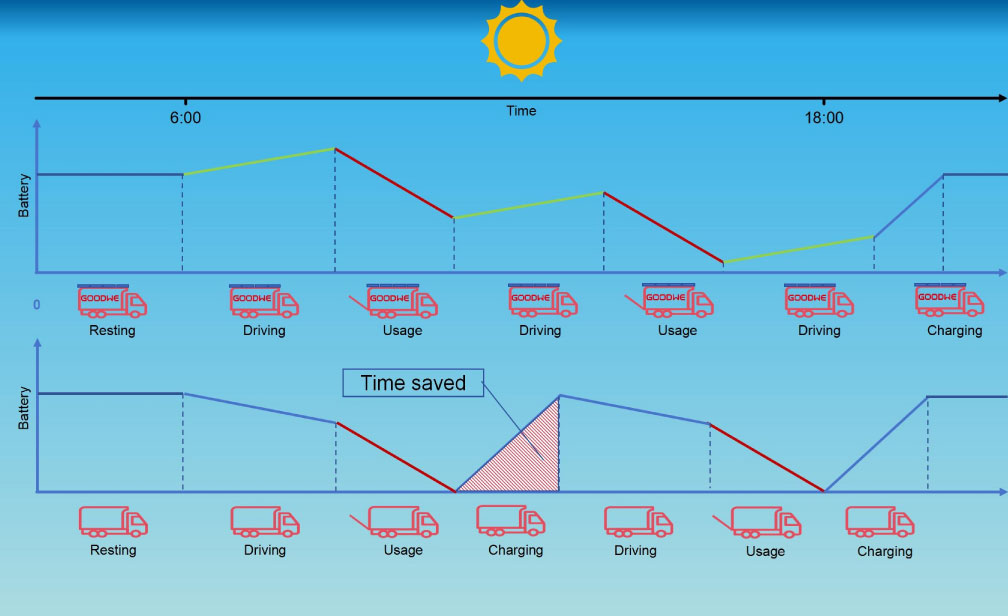
Picture 2. The electricity consumption curves of cold chain vehicles with and without Galaxy system
3.2 Advantage over combustion engine power system
In the field of cold-chain transportation, the comparison between traditional internal combustion engine power generation (relying on diesel generators) and rooftop PV power generation highlights multiple advantages of photovoltaic technology. In Australia, combustion engine power generation not only requires continuous consumption of diesel (the price of diesel in Australia is as high as A$2.20 per liter, with an average daily operating cost exceeding A$35), but also increases maintenance costs (about A$1,500 per year on average) due to frequent starts-and-stops and mechanical wear. In contrast, the PV system utilizes Australia's abundant sunshine resources, It directly replaces 27.5% of the air-conditioning energy consumption, saving a lot in fuel expenses annually. Additionally, when combined with energy storage, the photovoltaic system can support the continuous operation of the refrigeration system, reducing the risk of cargo damage and creating additional revenue through pre-cooling and improved loading and unloading efficiency. PV technology comprehensively outperforms the traditional internal-combustion-engine model in terms of economy (short-term payback), environmental friendliness (zero emissions), and operational stability (no shutdown risk), becoming the core approach for the low-carbon transformation of the world's cold-chain industry.
Picture 3. ROI Curve
Global Cold Chain Vehicle Market Growth
Global Data:
In 2023, the global stock of refrigerated trucks exceeded 4 million, with an annual growth rate of 11.2% (Source: Grand View Research). The European Union requires the proportion of renewable energy in the transportation industry to increase from 14% to 29% by 2030, and refrigerated trucks fall within this framework (Source: Renewable Energy Directive (RED III)).
Regional Opportunities:
China: The cold - chain logistics market is worth 550 billion yuan, and the penetration rate of new - energy refrigerated trucks is less than 5%.
North America: Plans to achieve net - zero carbon emissions for 50% of freight transportation (including cold - chain logistics) by 2030, and invests in electric trucks, renewable fuels, and energy - efficiency technologies.
Southeast Asia: Frost & Sullivan has released multiple analyses of the Southeast Asian cold-chain logistics market. For example, its 2023 report pointed out that the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of the Southeast Asian cold-chain logistics market is approximately 22%-24%, with fresh food e-commerce contributing over 40% of the incremental demand. Meanwhile, the Cold Chain Association of Southeast Asia (CCA) mentioned that the annual growth rate of the stock of refrigerated trucks in Indonesia, Vietnam, and Thailand is 20%-25%, mainly due to the increasing penetration rate of fresh food e-commerce.
Market Potential for Galaxy Products
Calculated based on a 5% photovoltaic modification rate for global refrigerated trucks, the current market size of refrigerated trucks is: 4 million × 5% × 12,000 dollars/truck = 2.4 billion dollar. GoodWe's Galaxy system directly addressed the energy pain points of cold-chain transportation. We hope to create customized solutions through Galaxy's patents, providing operators with an upgraded choice that combines economic efficiency and sustainability. Driven by the dual wheels of global zero-carbon policies and TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) optimization, GoodWe Galaxy will become the preferred technical partner for the new - energy transformation of refrigerated trucks.
Conclusion
Driven by innovation and aligned with global sustainability mandates, GoodWe’s Galaxy Series redefines cold chain vehicle energy solutions, ensuring operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced environmental responsibility. GoodWe remains committed as a trusted partner in facilitating the green energy transition within the cold chain logistics sector.